1. What is Penetrating Keratoplasty (PK)?
When all the layers of cornea is removed and replaced with healthy cornea, it is called as PK. PK was the very first successful organ transplant performed in humans. PK is 100 years old surgery.
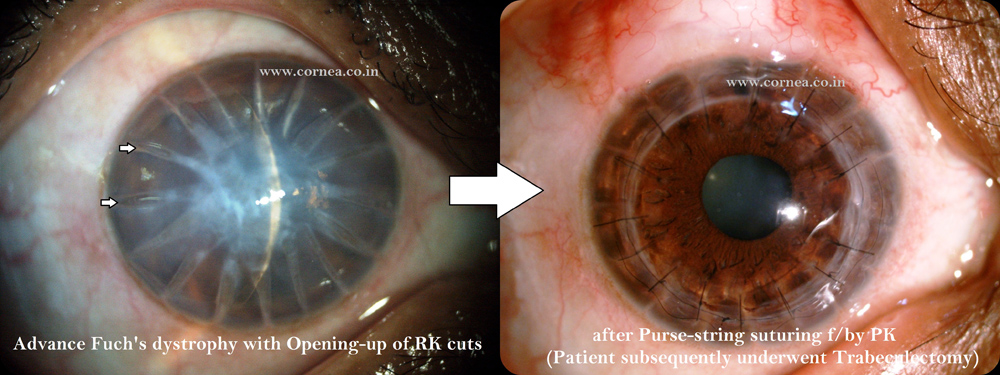
2. If lamellar corneal transplant (eg, DALK and DSEK) are superior to PK, then why is it still being practiced?
Sometimes patients have diseases in all the layers of the cornea. These patients need full thickness corneal transplant i.e, PK.
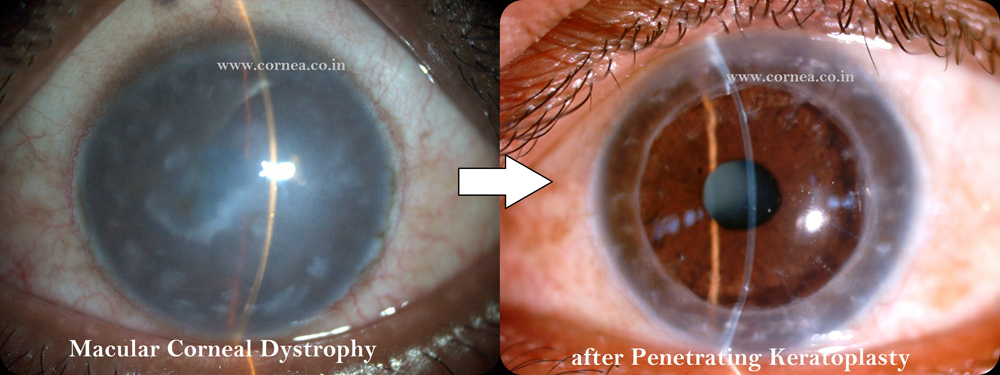
3. Are there higher chances of rejection in PK, compared to DSEK & DALK?
Yes. PK carries higher chance of immune rejection, due to replacement of all the layers of cornea.
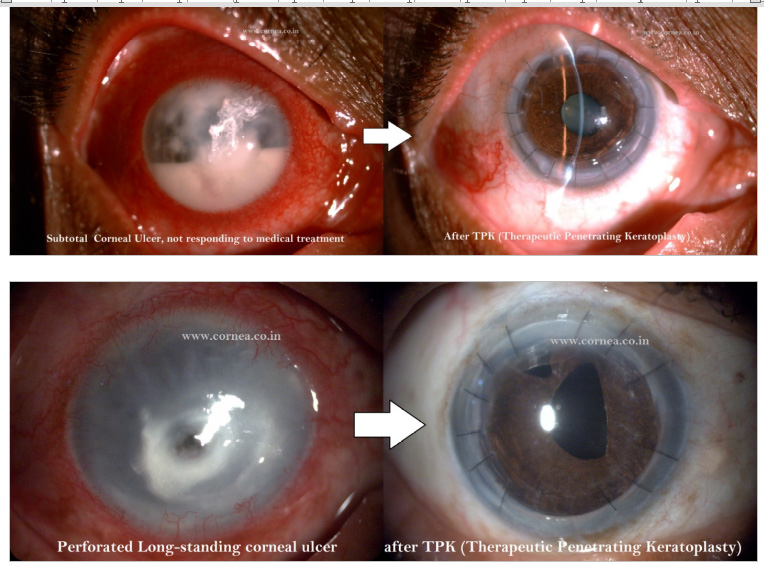
4. What is rejection and why does it occur?
Rejection is the immunological destruction of cornea. Rejection is usually acute and many a times it can be reversed with intensive therapy. The term “graft rejection” refers to the specific immunologic response of the host to the donor cornea. Because it is a specific process, it should be distinguished from other causes of “graft failure” that are not immune mediated.
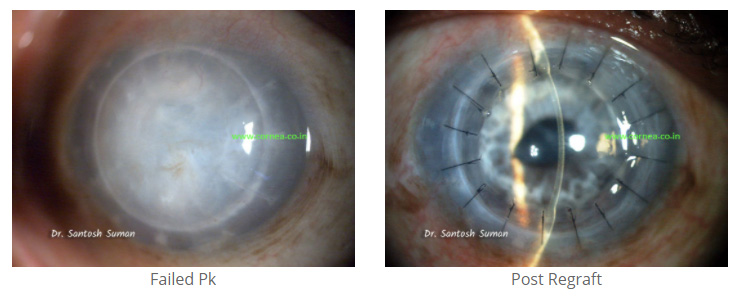
5. What are the signs of rejection?
Signs of rejection can be remembered as an acronym: R.S.V.P.
R: Redness
S: Sensitivity to light
V: Vision loss
P: Pain
Signs of rejection can be remembered as an acronym: R.S.V.P. R: Redness S: Sensitivity to light V: Vision loss P: Pain
If the patient suddenly experiences increase in redness, pain, watering of the operated eye or a drop in vision in the same eye, he/ she should immediately consult nearest cornea surgeon, preferably on the same day. Early graft rejection and early graft infection both can present similarly, but the treatment for both are exactly opposite.
7. I lost sight from a corneal scar in childhood. Now I am older. Will corneal transplant help me?
If vision is not restored before the age of 10, the brain begins to ignore that eye. This process is called “Amblyopia” or “Lazy Eye”. If dense amblyopia has settled, there is very less chance of visual improvement after corneal transplant.